Overview About Oligoscan
Intra Cellular Testing
Why Intracellular Testing is Important
Assess True Nutritional Status
Unlike serum (blood) tests that measure circulating nutrients at a moment in time, intracellular tests reveal long-term nutrient storage and utilization. This gives a better picture of whether the body is benefiting from the nutrients consumed.
Detect Hidden Deficiencies
Essential minerals and vitamins can be deficient even when blood levels seem normal. Intracellular testing helps uncover imbalances that could lead to chronic health issues.
Optimize Cellular Function
Cells need the right balance of nutrients to function correctly. Intracellular testing identifies deficiencies that might hinder energy production, DNA repair, and immune defense.
Monitor Heavy Metal Toxicity
Exposure to heavy metals (like lead, mercury, cadmium, and arsenic) can disrupt enzyme function, damage cells, and interfere with nutrient absorption. Intracellular testing helps detect toxic metal buildup before symptoms become severe.
Personalized Nutrition Plans
The results of intracellular testing can guide healthcare providers in tailoring diets, supplements, and detoxification strategies to address individual needs.
Oligoscan measure four point of your hand epiderm.
It is fast, non-invasive and results generate in minutes.
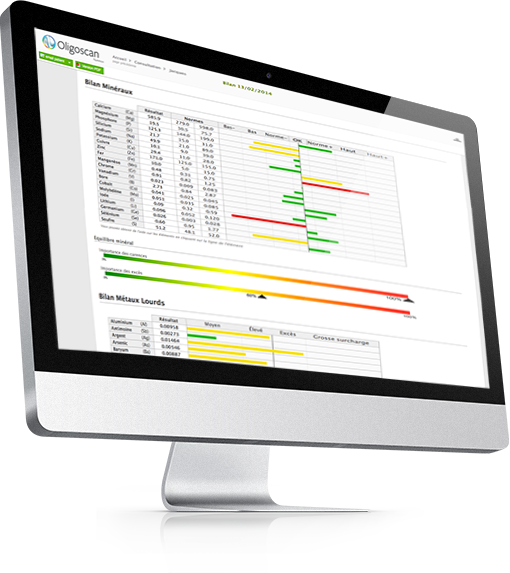
What OligoScan Test Measures
21 Essential Minerals, including:
Calcium: Vital for bone health and muscle contraction.
Magnesium: Supports energy production and nerve function.
Potassium: Regulates fluid balance and electrical signaling in the body.
Iron: Critical for oxygen transport in red blood cells.
Zinc: Strengthens immunity and aids cellular repair.
Selenium: An antioxidant that protects cells from damage.
7 Vitamins, including:
Vitamin D: Regulates calcium absorption and immune function.
Vitamin B12: Supports nerve function and red blood cell production.
Folate: Essential for DNA synthesis and repair.
Vitamin C: Boosts immunity and acts as an antioxidant.
Vitamin E: Protects cells from oxidative stress.
16 Heavy Metals, including:
Lead: Associated with neurological damage and developmental delays.
Mercury: Toxic to the brain, kidneys, and immune system.
Arsenic: Linked to cancer and cardiovascular issues.
Cadmium: Affects kidney function and bone health.
Applications of Intracellular Testing
Chronic Conditions: To identify nutrient deficiencies that contribute to diseases like fatigue, autoimmune disorders, or cardiovascular problems.
Athlete Optimization: To ensure adequate nutrient levels for performance and recovery.
Detox Programs: To monitor progress in removing heavy metals and restoring cellular health.
Preventative Health: To detect potential deficiencies or toxicities before symptoms arise.